Introduction to the Great Pyramids
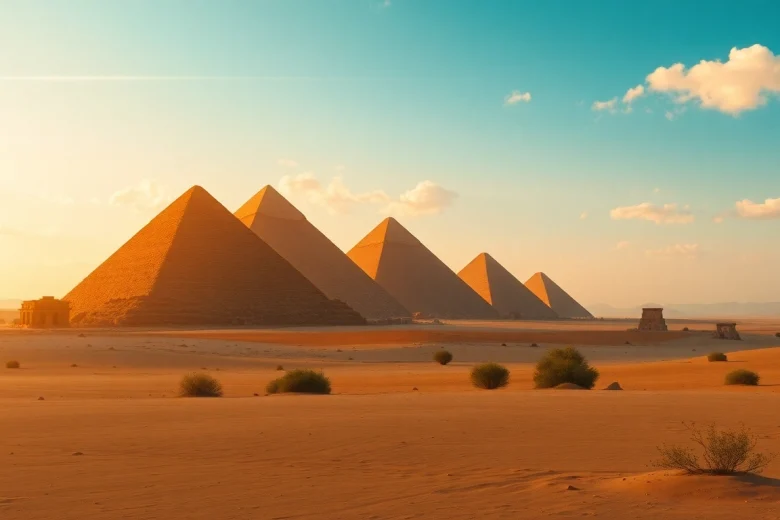
The Great Pyramids of Egypt stand as monumental testaments to the artistry, ingenuity, and cultural significance of ancient civilizations. These iconic structures, particularly the Pyramids of Giza, have fascinated historians, archaeologists, and travelers alike. Each pyramid represents not just a tomb but a complex interplay of faith, political power, and architectural prowess. The enduring allure of these structures can be explored on various platforms, including https://piraminds.com/, where insights into the history, construction, and mysteries surrounding them are brought to light.
Overview of the Great Pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids were primarily built as tombs for pharaohs and served various religious purposes. The most famous pyramids are the three located on the Giza Plateau, which include the Great Pyramid of Giza, built for Pharaoh Khufu, along with the pyramids of Khafre and Menkaure. Constructed during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, these structures are remarkable not only for their sheer size but also for their sophisticated design. At their peak, the Great Pyramid reached approximately 146.6 meters but now stands at around 138.8 meters due to the loss of the outer casing stones.
Historical Context and Construction
The construction of the Great Pyramids dates back to around 2580–2560 BCE. The era was marked by significant advances in engineering and architecture, facilitated by a strong centralized government. The construction process was labor-intensive; thousands of skilled laborers, artisans, and seasonal workers were mobilized. Rather than slaves, evidence suggests workers were well-fed and housed nearby, operating within a highly organized labor system. Materials such as limestone and granite were quarried, transported, and precisely placed using tools such as copper chisels, wooden sleds, and levers.
Significance in Ancient Egypt
The significance of the pyramids extends beyond their function as tombs. They are a testament to the Egyptians’ beliefs in the afterlife and the divine right of pharaohs. The pyramids symbolized the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife and their central role in ensuring the continued prosperity of the state. The elaborate burial practices and the treasures placed within the tombs highlighted the societal hierarchy and the paramount importance of death and the afterlife in sustaining life on Earth.
Pyramid Types and Structures
Understanding Different Pyramid Designs
Pyramids were not all built in the same style. Various types emerged over centuries, ranging from the step pyramid design to the smooth-sided pyramids seen at Giza. The earliest known pyramid is the Step Pyramid of Djoser at Saqqara. This revolutionary design features a series of mastabas (flat-roofed rectangular structures) stacked on top of one another, culminating in a six-tier structure. In contrast, the Giza pyramids feature a smoother outer casing, which reflects a move towards more refined construction techniques.
The Role of Purpose in Structure
The function of a pyramid heavily influenced its design. While the primary purpose was to serve as a burial site, the structures also included temples for services and rituals associated with the deceased. Some pyramids were incorporated into larger complexes that included mortuary temples and smaller tombs for family members, signifying the multifaceted purpose of these architectural marvels. This functionality showcases the Egyptians’ dedication to their rulers’ dignity in life and death.
Variations in Pyramid Construction Techniques
Over time, construction techniques evolved significantly. The transition from the stepped pyramid to the smooth pyramid involved innovations in design and expendable resources. The Giza pyramids showcase a highly advanced understanding of geometry and engineering; builders often aligned the structures with astronomical events, providing a deeper meaning to their locations. Various hypotheses exist on how the massive stone blocks were transported and precisely placed, including theories regarding ramps and counterweights.
Exploring Key Theories
Theories on Construction Methods
Many theories surround the construction methods of the pyramids. Some argue that a straight or zig-zagging ramp was used to move stones into position, while others propose a circular ramp that gradually spiraled around the structure. Recent discoveries suggest that a significant workforce fundamentally relied on community labor and participation rather than sheer force, providing insights into the socio-political structure of ancient Egypt.
Modern Discoveries and Archaeological Findings
Recent archaeological discoveries continue to shed light on the construction of the pyramids. New technologies, such as ground-penetrating radar, have revealed hidden chambers beneath the Giza plateau, suggesting that the pyramids may hold more secrets than previously thought. Ongoing excavations and studies deepen our understanding of the labor force, materials used, and even the daily lives of those who built these magnificent structures.
Theories Around Pyramid Functions
The theoretical functions of the pyramids indicate they served as more than just tombs. Some researchers hypothesize that they were designed to facilitate the pharaoh’s journey to the afterlife or acted as beacons connecting the earthly realm with the divine. This perspective reflects the intricate belief systems that dominated ancient Egyptian culture and illustrates how architecture served to bridge cultural and spiritual gaps.
The Cultural Impact of the Pyramids
Pyramids in Egyptian Mythology
The Great Pyramids are deeply embedded in Egyptian mythology, where they symbolize immortality and resurrection. The pharaoh was seen as a god on Earth, and the pyramids functioned as a means for the deity to ascend to the heavens upon death. Myths surrounding Osiris, the god of the afterlife, often drew parallels with the pyramids, highlighting a belief in cosmic renewal through death.
Representation in Art and Literature
Throughout history, the pyramids have inspired countless works of art and literature, becoming symbols of mystery and power. Ancient texts often referenced the architectural wonders, while modern depictions in films and literature continue to explore their enigma. This ongoing fascination ensures that the pyramids remain a significant subject in cultural narratives worldwide.
Influence on Modern Architecture and Culture
The architectural legacy of the Egyptian pyramids is evident in modern structures. Elements such as grand entrances, symmetry, and monumental scale have influenced various architectural styles across cultures. Many contemporary buildings, monuments, and memorials draw inspiration from the pyramids, underscoring their lasting impact on global architecture and reminding us of humanity’s enduring quest for permanence and meaning.
Visiting the Pyramids Today
Understanding Tourism at the Pyramids
The pyramids attract millions of tourists annually, making them one of the most visited archaeological sites. Tourist facilities around Giza, including guided tours and informative exhibitions, cater to a global audience eager to connect with ancient history. However, this influx of visitors necessitates careful management to preserve the integrity of the site.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Efforts to conserve the pyramids face numerous challenges, including environmental degradation, pollution, and the threat of structural damage from heavy tourism. Collaborations between governments, archaeological organizations, and local communities focus on implementing sustainable practices. Protecting these ancient monuments requires balancing tourist access with preservation methodologies to ensure their protection for future generations.
Future Perspectives on Pyramid Preservation
Looking forward, the future of pyramid preservation hinges on integrating technology with traditional conservation methods. Innovations such as 3D scanning and monitoring systems can facilitate ongoing research and conservation efforts. Through continuous engagement, education, and responsible tourism, we can safeguard these cultural treasures while allowing them to inspire awe and curiosity in visitors worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What were the pyramids used for?
The pyramids primarily served as monumental burial sites for pharaohs and were integral to their afterlife beliefs, symbolizing a connection to the divine.
How were the pyramids built?
Pyramids were constructed using a large workforce of skilled laborers, utilizing advanced techniques for transportation and lifting massive stones, often involving ramps.
What are the main pyramids in Egypt?
The most famous pyramids are those on the Giza Plateau, which include the Great Pyramid of Giza, Pyramid of Khafre, and Pyramid of Menkaure, all built during the Fourth Dynasty.
Why are the pyramids of Giza so significant?
The pyramids of Giza are significant due to their architectural innovation, cultural importance in ancient Egypt, and their symbolic representation of the pharaohs’ divine status.
Can you visit the pyramids today?
Yes, the pyramids are open to visitors, and various tours are available. However, efforts are made to manage tourism to protect these ancient structures.