The Marvel of the Pyramids: An Introduction
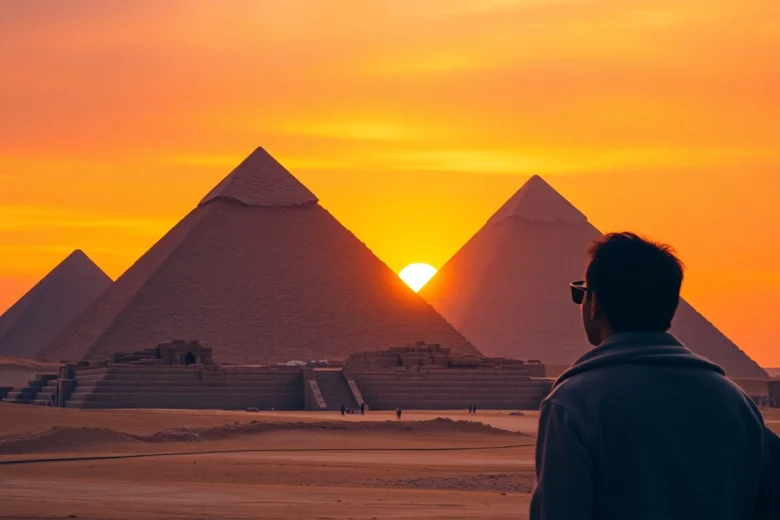
The pyramids stand as monumental testaments to ancient Egypt’s architectural prowess and the rich tapestry of its history. These iconic structures, especially those at Giza, have captivated generations of historians, archaeologists, and curious travelers alike. Spanning over four millennia, the pyramids not only symbolize the might of the pharaohs but also evoke a sense of mystery and intrigue that compels exploration and study. For those eager to delve deeper into the wonders of the pyramids, https://piraminds.com/ serves as an invaluable resource.
What are the Pyramids?
The pyramids, primarily located in Egypt, are ancient structures characterized by their triangular shape, built as elaborate tombs. The most famous is the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World that remains largely intact. These structures served to house the remains of pharaohs, providing them with a safe passage to the afterlife and reflecting their power and divinity.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of the pyramids extends beyond their architectural brilliance; they are a manifestation of ancient Egyptian beliefs surrounding death and the afterlife. Constructed during the Old and Middle Kingdoms, these structures were part of a larger religious and cultural narrative that defined the era. The pyramids served not just as tombs but as symbols of eternal life and the chance for resurrection in a divine realm.
Pyramid Complexes Explained
Pyramid complexes are more than just the pyramids themselves; they are intricate assemblies of structures. These typically include mortuary temples, smaller pyramids for queens, and massive walls encircling the complex. The organization of these complexes reflects the sophisticated planning and resources of the ancient Egyptians, who viewed the afterlife as just as important as earthly existence.
Constructing the Wonders: How Were They Built?
Ancient Engineering Techniques
The construction of pyramids showcases the advanced engineering practices of ancient Egyptians. Techniques such as leveraging levers, ramps, and counterweights allowed workers to transport and position massive stone blocks, some weighing several tons. The precision required in aligning these structures indicated a profound understanding of mathematics and astronomy.
The Tools and Materials Used
Ancient Egyptians employed tools made from copper, stone, and wood. Simple tools like chisels and mallets played a crucial role in shaping limestone and granite blocks. The primary materials, limestone and granite, were quarried from nearby locations, with granite being primarily sourced from Aswan. The choice of material represented both functionality and symbolism, as limestone, for example, mirrored the sun’s brightness.
Labor Force Behind the Pyramids
The building of the pyramids was no small feat; it required a massive labor force comprised of skilled laborers, craftsmen, and seasonal workers. Contrary to the popular belief that slaves built the pyramids, recent evidence indicates that the workforce was organized, well-fed, and reflected a society that valued labor as part of national pride and duty.
Mythology and Mystique Surrounding the Pyramids
Legends and Theories
The pyramids have long been shrouded in legends and mystical theories. From tales of ancient aliens to advanced technologies lost to time, the narrative surrounding their construction often borders on the fantastical. Scholars debate various theories, yet many emphasize the ingenuity of the ancient Egyptians as the primary source of their construction prowess.
What Lies Inside?
Inside the pyramids, intricate passageways and chambers tell a story of ritual and reverence to the deceased rulers. The burial chamber typically contains the sarcophagus of the pharaoh, surrounded by treasures meant to accompany and protect them in the afterlife. Hieroglyphics and artwork adorning the walls serve not just as decoration but as inscriptions of the deceased’s life and aspirations for eternity.
Pyramids in Popular Culture
The grandeur of pyramids has permeated popular culture, inspiring countless films, books, and artworks. They are often depicted as symbols of mystery and adventure, capturing the imagination of people around the world. Their portrayal in media emphasizes the enduring fascination with ancient civilizations and the legacy left behind.
Visiting the Pyramids: What to Expect
Travel Tips for Tourists
For travelers keen on experiencing the pyramids firsthand, it’s essential to plan ahead. Visiting in the cooler months (October to April) can enhance the experience, making exploration more comfortable. Choosing the right time of day, early morning or late afternoon, can also provide stunning light for photography while avoiding the heat.
Guided Tours and Experiences
Opting for a guided tour can enrich the visit, providing historical context and insights that self-guided tours may lack. Many professionals offer tailored experiences, including sunrise horseback rides or private tours that delve into lesser-known stories of the pyramids, allowing for a deeper appreciation of these ancient wonders.
Cultural Etiquette and Respect
When visiting the pyramids, it’s crucial to respect local customs and regulations. Visitors should dress modestly, be mindful of photography restrictions, and always follow the guidance of official tour guides to preserve the sites. Engaging with local culture, including trying traditional food or participating in rituals, can enhance the travel experience.
FAQs About the Pyramids
1. How old are the Pyramids?
The Pyramids of Giza date back to around 2580–2560 BC during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom of Egypt.
2. Why were the Pyramids built?
Pyramids served as colossal tombs aimed at ensuring a safe passage of pharaohs into the afterlife.
3. Can you enter the Pyramids?
Yes, certain pyramids allow visitors inside, offering a glimpse into their interior designs and chambers.
4. What is the best time to visit?
Spring (March to May) and autumn (September to November) offer milder temperatures and fewer crowds for visitors.
5. Are the Pyramids aligned with the stars?
Yes, many structures’ alignment was influenced by astronomical events and the stars prominent in their culture.