Understanding the Historical Significance of the Pyramids
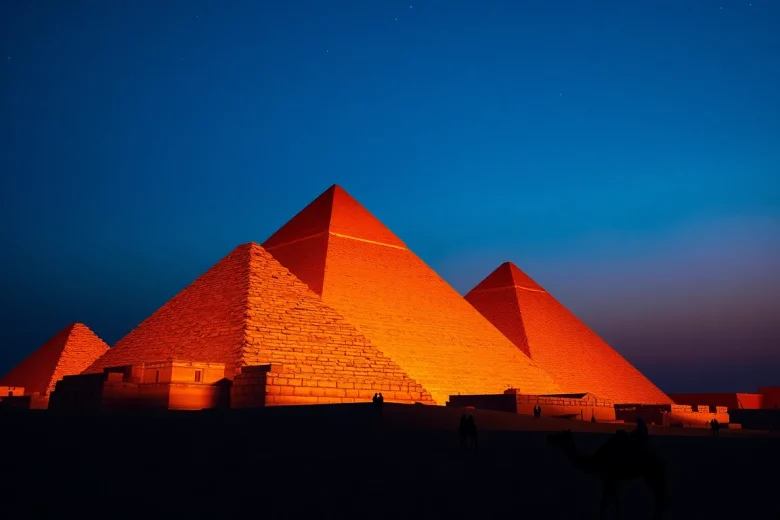
The pyramids of Egypt represent some of the most extraordinary architectural feats in human history, serving not just as tombs for pharaohs but also encapsulating the rich mythology and cultural beliefs of ancient Egyptian civilization. As you delve into their captivating narratives, you can discover more about these magnificent structures at https://piraminds.com/.
The Origins and Purpose of the Pyramids
The Egyptian pyramids primarily served as monumental tombs for pharaohs who ruled during the Old and Middle Kingdom periods. The earliest pyramid, the Step Pyramid of Djoser, built around 2630 BCE, showcases the evolution of tomb architecture from simple mastabas to grand pyramids. They were designed to ensure the deceased pharaoh’s safe passage into the afterlife, a belief deeply rooted in ancient Egyptian religion.
Cultural Impact on Ancient Egyptian Society
Pyramids are deeply interwoven with the socio-political fabric of ancient Egypt, representing centralized power and religious belief. They served not merely as burial sites but as symbols of the divine nature of the pharaoh’s rule. The labor force that constructed these pyramids included skilled workers, craftsmen, and seasonal laborers, which profoundly affected the economy and social structures, fostering a sense of unity and purpose among the Egyptian populace.
Symbolism in Architecture and Funerary Practices
The design of the pyramids is steeped in symbolism. Their geometric shape represents the rays of the sun, functioning as a conduit for the pharaoh’s ascent to the divine. Furthermore, the interior chambers and sarcophagi were intricately decorated with hieroglyphics and spiritual artifacts aimed at guiding the pharaoh in his eternal journey, thus providing critical insight into ancient Egyptian beliefs about life after death.
Current Discoveries and Archaeological Advances
Recent Findings at Giza and Surrounding Areas
Excavations at Giza and the surrounding necropolis have unearthed several groundbreaking discoveries. Over the last few years, remote sensing technologies have revealed hidden structures beneath the ground, suggesting that Giza was a far more complex site than previously understood. The use of drones and 3D scanning techniques are leading to more accurate maps of the pyramids and their surroundings, facilitating a deeper understanding of their construction and purpose.
Technological Innovations in Archaeology
Modern archaeology has embraced technology in unprecedented ways. Advanced tools such as ground-penetrating radar and photogrammetry allow researchers to visualize subsurface features without excavation. These innovations provide valuable data about the site’s layout, including potential unexcavated tombs and artifacts, thereby minimizing the disturbance to this delicate heritage site.
Comparison of Ancient Techniques with Modern Methods
The construction of the pyramids involved remarkable engineering prowess, using rudimentary tools that were well-adapted to the geology of the region. In comparison, modern methods emphasize data collection, mapping, and preservation techniques. While ancient builders relied on human labor and simple sleds to move massive stones, contemporary techniques utilize machinery and scientific analysis to decipher their methods, all while striving to preserve what remains.
Visitors’ Guide to the Pyramids
Best Times to Visit and Experience
The ideal times to visit the pyramids are during the cooler months of the year, from November to March, when temperatures are more bearable for sightseeing. Early mornings or late afternoons are particularly appealing, offering not only a comfortable visit but also beautiful lighting for photography, enhancing the experience of standing in the shadows of these colossal structures.
What to Expect: Tours and Guided Experiences
Visitors can expect a variety of tour options, ranging from guided group tours to private experiences offering deeper insights into the history and significance of each pyramid. Most tours highlight key sites, including the Great Pyramid of Giza, the Sphinx, and the nearby Valley of the Kings. Engaging tour guides often share fascinating anecdotes and recent archaeological findings, enriching the visitor experience.
Local Etiquette and Cultural Considerations
When visiting the pyramids, being respectful of the local culture is paramount. Dress modestly, particularly when entering religious sites, and always seek permission before photographing people. Understanding the significance of the pyramids within Egyptian culture can enhance your experience and foster greater respect for this ancient civilization.
Challenges in Preserving the Pyramid Structures
Environmental Threats and Conservation Efforts
The preservation of the pyramids faces significant challenges, including environmental degradation from pollution and climate change. The Egyptian government, alongside various international organizations, is actively involved in conservation efforts which include monitoring structural integrity and implementing protective measures around the sites to ensure their longevity for future generations to appreciate.
Impact of Tourism on Preservation
While tourism plays a crucial role in funding conservation initiatives, it also poses a threat to the integrity of the pyramids. Increased foot traffic and temperature fluctuations due to large tourist groups can lead to accelerated wear. Sustainable tourism practices are being developed to balance visitor access with the preservation needs of these ancient sites, ensuring that they can be experienced without compromising their structural integrity.
Collaboration between Governments and Organizations
Efforts to preserve the pyramids are often collaborative, involving local authorities, international governments, and UNESCO. Projects aimed at utilizing advanced technologies and sharing research findings not only contribute to preserving the pyramids but also foster international cooperation in protecting cultural heritage worldwide.
Future Research Directions on the Pyramids
Potential Discoveries Awaiting Outside Giza
Research continues to explore areas outside Giza, with experts theorizing the existence of undiscovered pyramids and burial sites. The application of new technologies, combined with traditional excavation, may yield exciting insights into the broader context of pyramid-building practices across ancient Egypt, significantly expanding our understanding of this civilization.
Interdisciplinary Approaches and Their Benefits
Interdisciplinary research combining archaeology, history, and even engineering is becoming crucial in the study of the pyramids. This collaborative approach not only enhances the methodology used to explore these ancient structures but also sparks innovative theories about their construction and historical context, ultimately providing a more comprehensive understanding of ancient Egyptian culture.
Global Interest and Funding for Continued Research
The global fascination with the pyramids ensures ongoing interest and funding for research projects. Donations from both private individuals and institutions, alongside increased public engagement through educational campaigns, are vital for sustaining long-term research projects and preservation efforts, which can reveal further insights into one of humanity’s most remarkable architectural achievements.
FAQs about the Pyramids
1. What are the main pyramids in Egypt?
The most famous pyramids are the Great Pyramid of Giza, along with the Pyramid of Khafre and the Pyramid of Menkaure, all located on the Giza plateau.
2. How were the pyramids constructed?
The pyramids were built using large limestone blocks, transported by workers using sledges and ramps, relying on advanced knowledge of engineering and team coordination.
3. Why were pyramids built as tombs?
Pyramids served as monumental tombs for pharaohs, reflecting their authority and spiritual beliefs about life after death, ensuring safe passage to the afterlife.
4. How can I protect the pyramids when visiting?
Visitors should respect guidelines, avoid climbing on structures, adhere to marked paths, and stay aware of local customs to help preserve the sites.
5. What are recent archaeological finds near the pyramids?
Recent discoveries include hidden tunnels and additional burial chambers, providing deeper insights into the construction and use of the sites dating back thousands of years.